Residential windows play a crucial role in enhancing both the aesthetic appeal and energy efficiency of a home. As noted by Dr. John Mason, a renowned expert in building materials and design, "The right residential windows can transform a house into a home, providing not only natural light but also comfort and style." Selecting the appropriate windows for residential properties is not merely about personal taste; it involves understanding the various types available, their unique benefits, and how they align with the overall design and functionality of the home.
The landscape of residential windows has evolved significantly over the years, offering a myriad of options from traditional wooden frames to modern vinyl selections. Each type presents its own set of advantages, such as energy efficiency, durability, and maintenance needs. Homeowners face the challenge of navigating these choices to find windows that not only suit their stylistic preferences but also stand the test of time in terms of performance and value. With the right information and guidance, the process of selecting residential windows can be a rewarding experience that enhances the livability and appeal of any home.

Residential windows play a crucial role in the overall functionality and aesthetics of a home. These windows are designed specifically for residential properties, serving multiple purposes such as providing natural light, enhancing ventilation, and ensuring security. They come in various styles and materials, allowing homeowners to choose options that best fit their architectural design and personal preferences. Common types of residential windows include single-hung, double-hung, sliding, casement, and awning windows, each offering unique characteristics that cater to different needs and environments.
When considering residential windows, it’s essential to evaluate their energy efficiency and insulation properties. Modern windows often feature advanced glazing technologies and frames that improve thermal performance, thereby reducing energy costs. Additionally, the right windows can significantly enhance the curb appeal of a home, adding to its market value. Factors such as local climate, maintenance requirements, and personal style should guide homeowners in selecting the most suitable windows. Ultimately, the right choice not only improves comfort and energy efficiency but also elevates the aesthetic quality of a residence.
When choosing residential windows, understanding the various styles and features is essential for optimizing energy efficiency, aesthetics, and functionality. One of the most common types is double-hung windows, which feature two sashes that can be moved up and down. This design enhances ventilation and allows easy cleaning. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, replacing single-pane windows with double-hung options can reduce energy costs by up to 30%, illustrating the financial benefits of selecting the right window type.
Another popular choice is casement windows, which are hinged on one side and open outward. These windows provide an unobstructed view and are known for excellent air circulation when positioned correctly. In climates with unpredictable weather, they effectively block wind and rain. Additionally, sliding windows offer a modern aesthetic and are ideal for spaces where a traditional swinging window may not fit. Their seamless operation adds to their appeal, ensuring ease of use.
Tips: When selecting windows for your home, consider factors such as insulation value (U-value and R-value) and local climate conditions. Installing ENERGY STAR rated windows can further enhance your home's energy performance. Moreover, ensure proper installation to prevent air leaks, which can offset the energy efficiencies of newer windows. Lastly, don’t overlook the importance of window frame materials—vinyl, wood, and fiberglass each offer unique benefits in terms of durability and maintenance.
This chart illustrates the distribution of common types of residential windows based on a survey of homeowner preferences, highlighting styles and features.
Upgrading residential windows brings a multitude of advantages that significantly enhance both the comfort and energy efficiency of a home. One of the most substantial benefits is improved insulation, which helps maintain consistent indoor temperatures throughout the year. Advanced window technologies, such as double or triple glazing, reduce heat transfer, ensuring that homes remain warm in winter and cool in summer. This not only contributes to a more pleasant living environment but also leads to reduced energy bills, as homeowners rely less on heating and cooling systems.
In addition to energy efficiency, upgraded windows can enhance a home's aesthetic appeal. Modern designs offer a variety of styles, colors, and finishes that can complement the overall architecture of a house, increase curb appeal, and potentially boost property value. Furthermore, many newer window options provide better noise reduction, allowing homeowners to enjoy a quieter living space. The integration of advanced security features in newer window models also provides peace of mind, making it harder for intruders to gain access to a home. Overall, the key benefits of upgrading residential windows resonate with homeowners seeking comfort, savings, and security.
| Window Type | Material | Energy Efficiency Rating | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Double-Hung Windows | Vinyl | U-Factor: 0.30 | Easy to clean, good ventilation, classic look |
| Casement Windows | Fiberglass | U-Factor: 0.27 | Excellent airflow, unobstructed view, high energy efficiency |
| Sliding Windows | Aluminum | U-Factor: 0.35 | Space-saving design, modern look, easy operation |
| Bay Windows | Wood | U-Factor: 0.29 | Enhances natural light, adds architectural interest, increased space |
| Picture Windows | Vinyl | U-Factor: 0.25 | Maximizes views, energy-efficient, fixed structure |
When choosing the right residential windows, several factors play a crucial role in making an informed decision. One of the primary considerations is the window material. Options such as vinyl, wood, fiberglass, and aluminum each offer different levels of insulation, durability, and aesthetic appeal. For example, vinyl windows are known for their energy efficiency and low maintenance, while wood windows provide a classic look but may require more upkeep. Understanding the climate of your area can also influence material choice, as some materials may perform better in specific weather conditions.
Another significant factor is the energy efficiency rating of the windows. Look for windows that are ENERGY STAR certified, which indicates they meet strict energy efficiency guidelines. These windows can help reduce heating and cooling costs and improve indoor comfort by minimizing drafts and heat transfer. Additionally, consider the type of glazing. Double or triple-pane glass with low-emissivity (Low-E) coatings can significantly enhance insulation and reduce UV exposure, further protecting your home’s interior. Lastly, consider the style and function of the windows, as they should complement the overall design of your home while meeting your practical needs for ventilation and natural light.
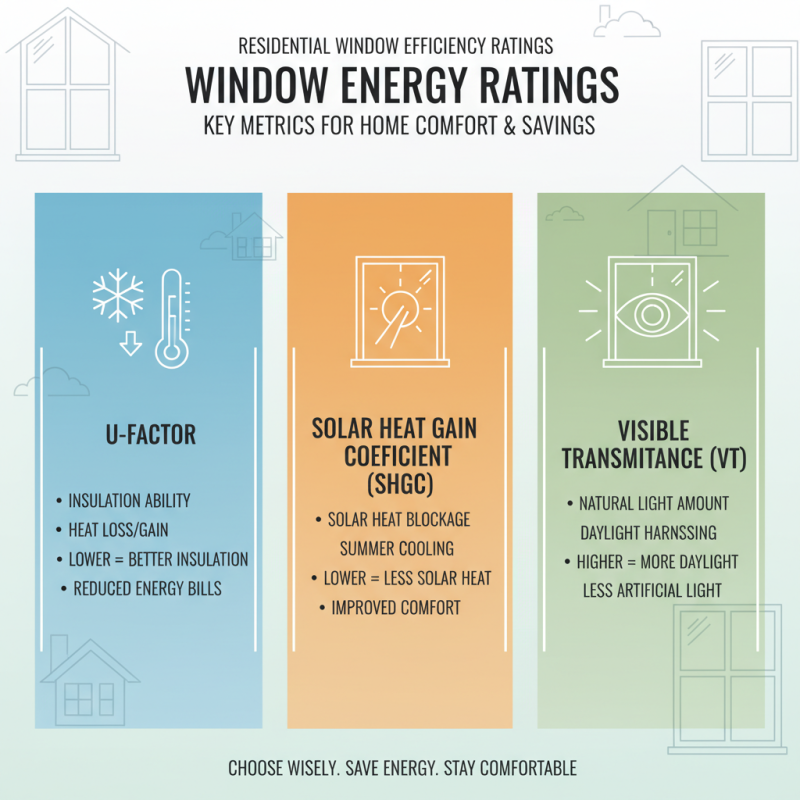
When choosing residential windows, one of the most crucial aspects to consider is energy efficiency ratings, which provide insights into window performance metrics. These ratings often include the U-factor, solar heat gain coefficient (SHGC), and visible transmittance (VT). The U-factor measures the window's insulation ability, indicating how much heat escapes or enters through the window. A lower U-factor means better insulation and reduced energy costs over time.
The solar heat gain coefficient (SHGC) reflects how much solar radiation is transmitted through the window. A higher SHGC is beneficial in colder climates where maximizing sunlight can help with heating, while a lower SHGC is preferable in warmer areas to minimize cooling costs. Lastly, visible transmittance measures the amount of light that passes through the window; higher values contribute to better natural lighting, reducing the need for artificial lighting. Understanding these metrics enables homeowners to select windows that not only enhance comfort but also lead to significant energy savings.